Understanding Stress and Anxiety: A Scientific Perspective
Stress and anxiety are natural physiological and psychological responses to challenging situations. While acute stress can enhance focus and reaction times, chronic stress can lead to cardiovascular disease, weakened immune function, hormonal imbalances, and mental health disorders such as depression and generalized anxiety disorder (GAD). Understanding the underlying neurobiology of stress is crucial to managing it effectively.
The Science Behind Stress: How It Affects the Brain and Body
The hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal (HPA) axis plays a key role in the body’s response to stress. When triggered by a perceived threat, the brain signals the adrenal glands to release cortisol and adrenaline, leading to an increased heart rate, heightened alertness, and suppressed digestion and immune functions.

Chronic activation of the HPA axis results in cognitive decline, increased inflammation, and mood disorders. Fortunately, neuroscience and psychology offer several evidence-based techniques to mitigate stress and restore homeostasis.
Evidence-Based Techniques to Reduce Stress and Anxiety
1. Mind-Body Interventions
a) Mindfulness Meditation & Deep Breathing
- Studies show that mindfulness-based stress reduction (MBSR) reduces amygdala activity (the brain’s fear center) and enhances prefrontal cortex function (responsible for rational thinking).
- Deep breathing techniques, such as diaphragmatic breathing (4-7-8 method), reduce cortisol levels and activate the parasympathetic nervous system, promoting relaxation.
b) Progressive Muscle Relaxation (PMR)
- A technique that involves systematically tensing and relaxing muscle groups, shown to lower blood pressure, heart rate, and anxiety symptoms.
c) Yoga & Tai Chi

- Both practices combine physical movement, breath control, and mindfulness, improving heart rate variability (HRV) and reducing chronic stress.
2. Neurological and Cognitive Techniques
a) Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT)
- CBT helps reframe negative thought patterns that contribute to anxiety. Studies show CBT is as effective as medication for treating generalized anxiety disorder and social anxiety.
b) Neurofeedback Therapy
- Uses EEG biofeedback to train individuals to regulate brainwave patterns associated with stress and anxiety.
c) Journaling & Expressive Writing
- Writing about emotions has been proven to enhance emotional regulation, reduce ruminative thoughts, and lower cortisol levels.
3. Lifestyle and Behavioral Modifications
a) Physical Exercise
- Regular aerobic exercise increases brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF), which enhances neuroplasticity and reduces stress hormones.
- Strength training and resistance exercises improve mood and reduce symptoms of anxiety disorders.
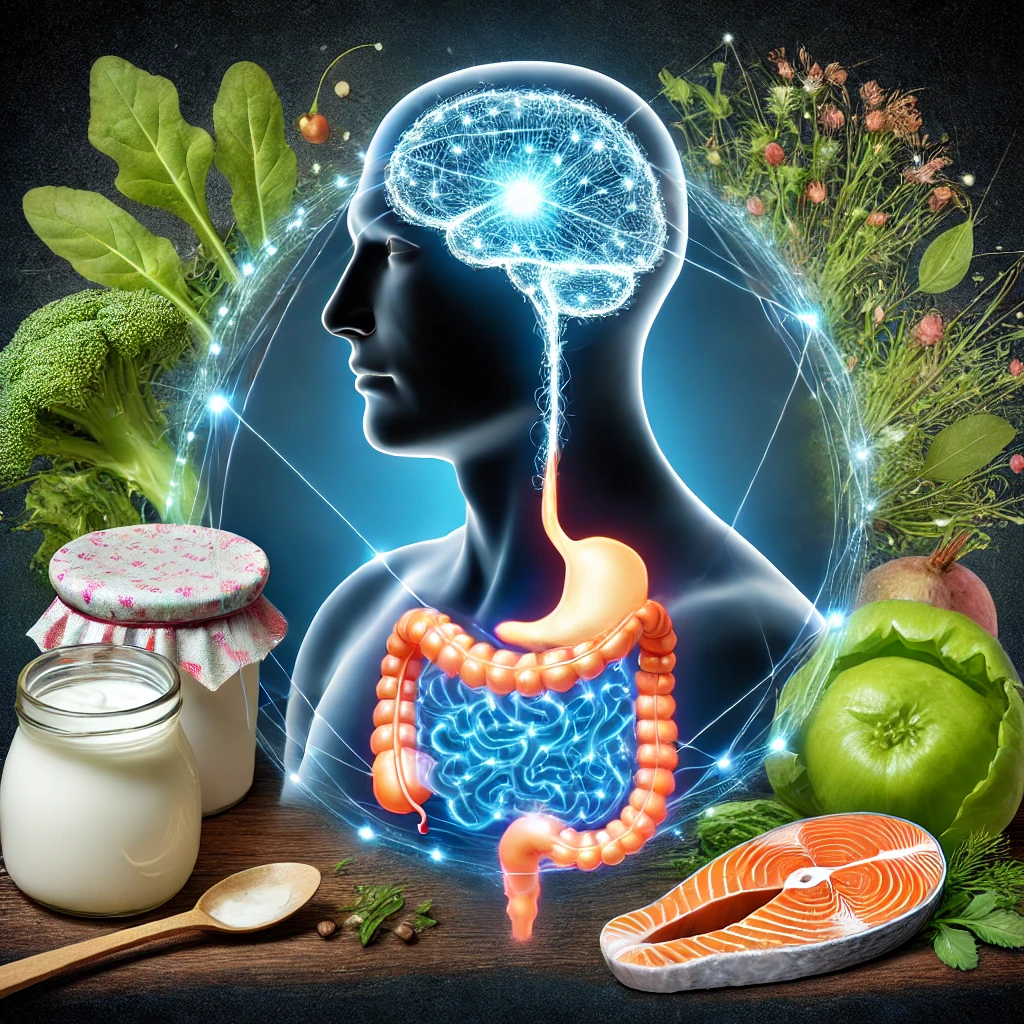
b) Nutrition and Gut Health
- The gut-brain axis plays a crucial role in emotional regulation. Diets rich in probiotics, omega-3 fatty acids, magnesium, and B vitamins support mental health.
- Limiting caffeine, alcohol, and processed foods reduces stress-inducing inflammation.
c) Sleep Optimization

- Chronic stress disrupts sleep patterns, leading to a vicious cycle of anxiety and sleep deprivation.
- Practices such as sleep hygiene, melatonin supplementation, and cognitive restructuring can enhance sleep quality.
4. Social and Environmental Approaches
a) Social Support Networks
- Studies indicate that strong social bonds activate the oxytocin system, reducing cortisol levels and promoting resilience.
b) Exposure to Nature (Ecotherapy)
- Research in environmental psychology demonstrates that spending time in green spaces, practicing forest bathing (Shinrin-yoku), or even viewing nature scenes can significantly lower stress hormones.
c) Aromatherapy & Sensory Stimulation
- Essential oils like lavender, chamomile, and bergamot influence the limbic system, promoting relaxation and reducing anxiety symptoms.
Final Thoughts: Creating a Holistic Stress-Reduction Plan
Managing stress and anxiety requires an integrative approach combining biological, psychological, behavioral, and social strategies. Experimenting with various techniques and identifying personal triggers can lead to a sustainable and long-term stress management routine.
By incorporating these scientifically validated methods into daily life, individuals can enhance mental clarity, emotional balance, and overall well-being. If stress persists despite lifestyle modifications, consulting a medical professional or mental health expert is recommended.
What’s Your Next Step?
Try implementing one technique from each category today and track its impact. Over time, small changes lead to significant improvements in resilience and stress tolerance.