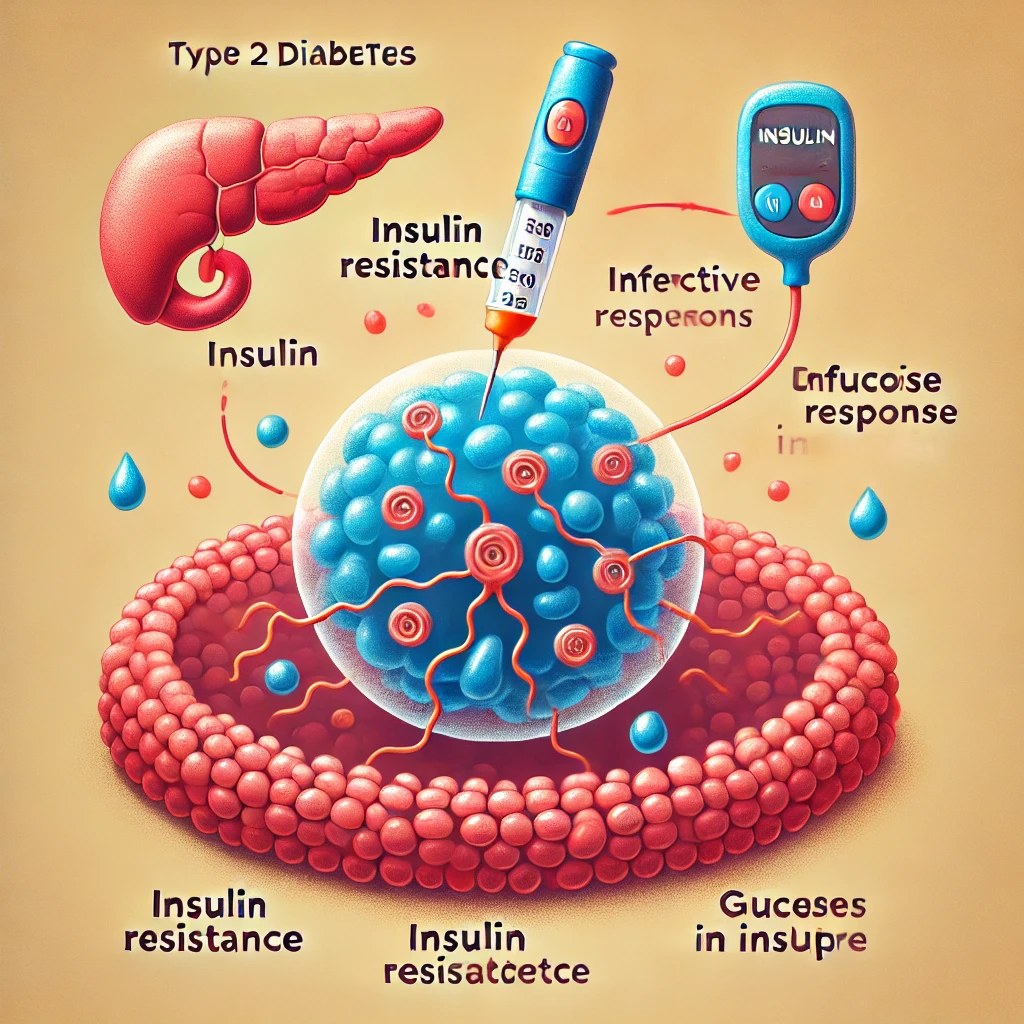
Type 2 diabetes is a chronic metabolic disorder that affects the way the body processes blood sugar (glucose). It occurs when the body becomes resistant to insulin or when the pancreas fails to produce enough insulin to maintain normal blood sugar levels.
Contents
Causes of Type 2 Diabetes
Several factors contribute to the development of type 2 diabetes, including:
- Insulin resistance – The body’s cells do not respond effectively to insulin.
- Genetics – A family history of diabetes increases the risk.
- Obesity – Excess body fat, especially around the abdomen, is a major risk factor.
- Sedentary lifestyle – Lack of physical activity contributes to insulin resistance.
- Poor diet – High sugar and processed food intake can lead to weight gain and insulin resistance.
- Age – The risk increases with age, typically after 45, though younger individuals are increasingly affected.
- Hormonal imbalances – Conditions like polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) can increase the risk.
Symptoms of Type 2 Diabetes
Many people have mild or no symptoms in the early stages. Common signs include:
- Increased thirst and frequent urination
- Unexplained weight loss or gain
- Fatigue and lack of energy
- Blurred vision
- Slow healing of wounds
- Frequent infections (e.g., skin or urinary tract infections)
- Numbness or tingling in the hands and feet (diabetic neuropathy)
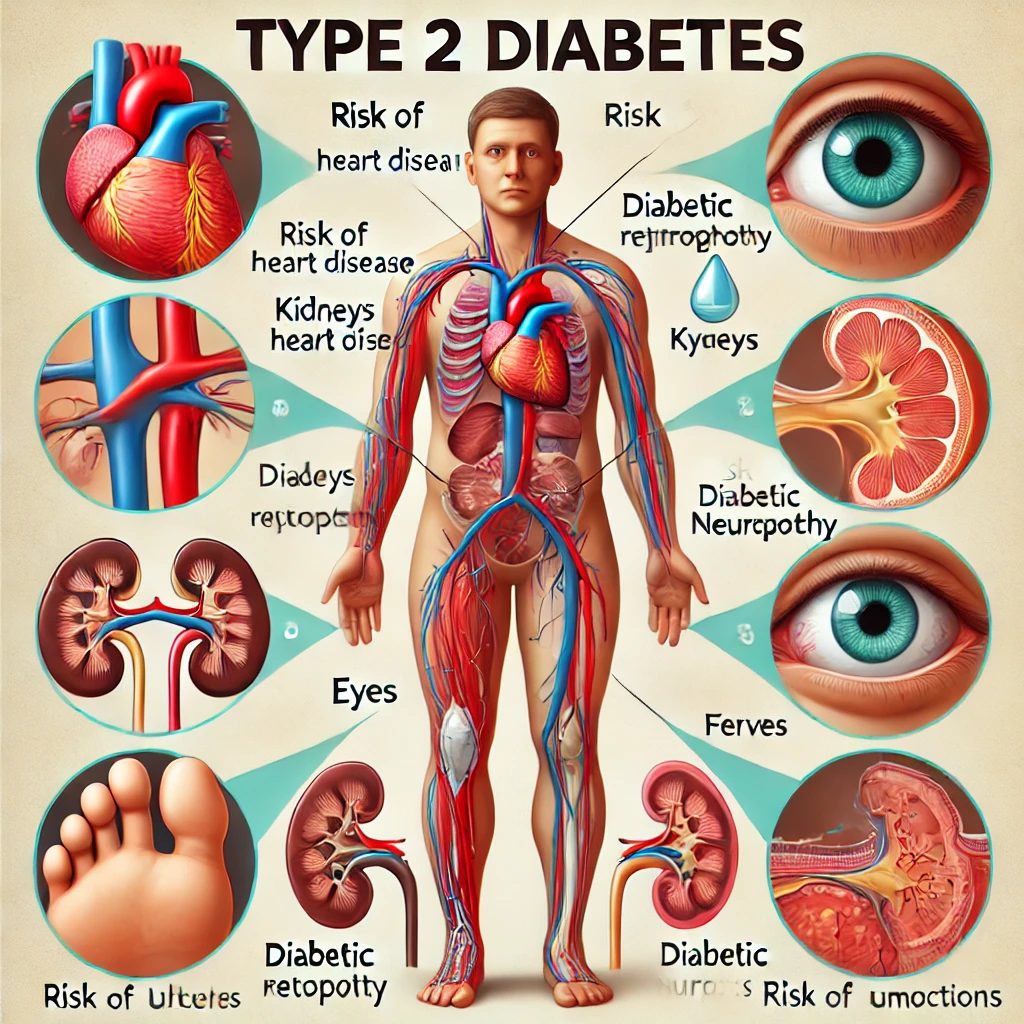
Complications of Type 2 Diabetes
If left untreated or poorly managed, type 2 diabetes can lead to serious complications, such as:
- Heart disease & stroke
- Kidney disease (diabetic nephropathy)
- Nerve damage (diabetic neuropathy)
- Eye problems (diabetic retinopathy, leading to blindness)
- Foot problems (infections, ulcers, possible amputations)
- Increased risk of infections
Management & Treatment
While there is no cure for type 2 diabetes, it can be managed through:
- Lifestyle changes:
- Healthy diet (low in sugar and refined carbs, high in fiber and protein)
- Regular exercise (at least 30 minutes of moderate activity most days)
- Weight loss (even a 5-10% reduction can improve blood sugar levels)
- Medications:
- Metformin – First-line medication to improve insulin sensitivity.
- Sulfonylureas – Help the pancreas produce more insulin.
- SGLT2 inhibitors & GLP-1 receptor agonists – Help lower blood sugar and sometimes promote weight loss.
- Insulin therapy – Required in advanced cases.
- Blood sugar monitoring:
- Regular testing to keep glucose levels in check.
- Stress management & sleep improvement:
- Stress and poor sleep can raise blood sugar levels.
Can Type 2 Diabetes Be Prevented?
Yes! You can reduce the risk by:
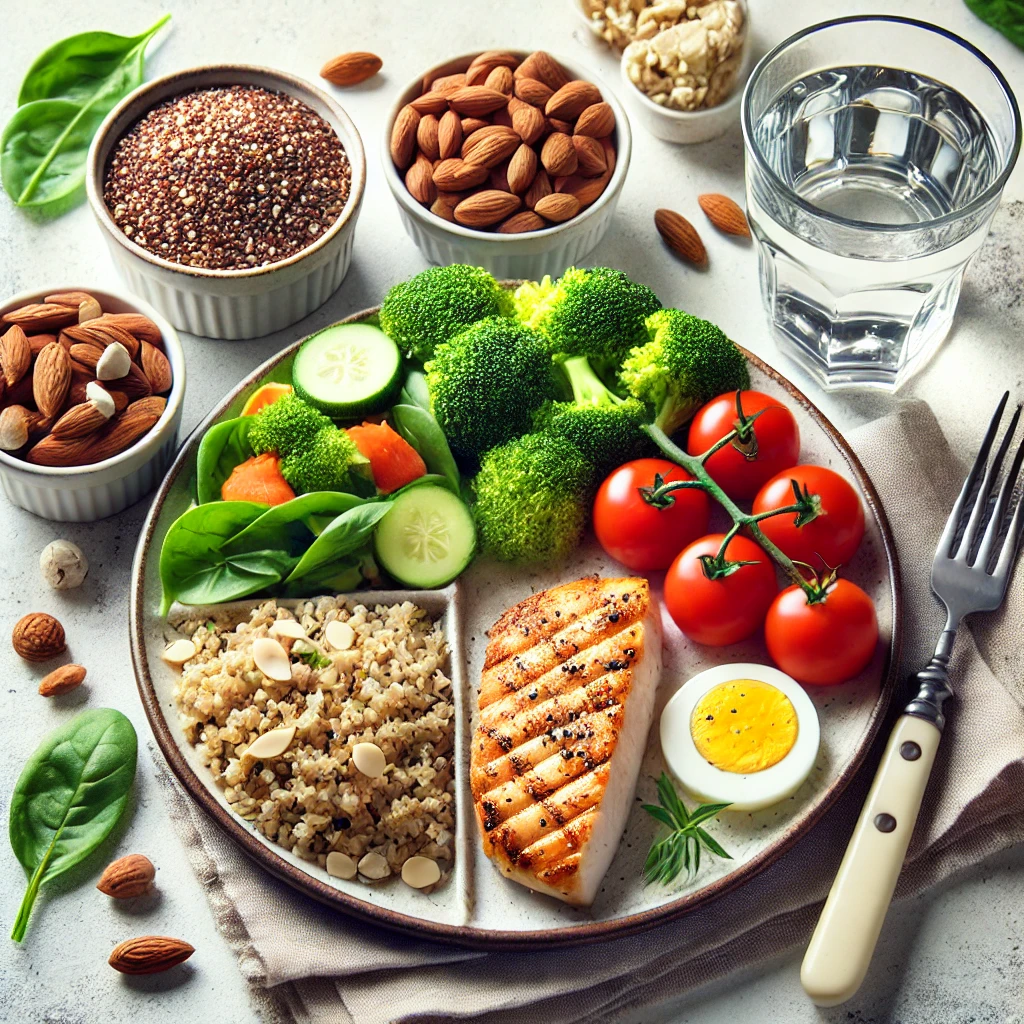

- Maintaining a healthy weight
- Eating a balanced diet (low sugar, high fiber)
- Being physically active
- Avoiding smoking and excessive alcohol
- Managing stress and getting enough sleep