Introduction
Leptin is one of the most critical hormones in human metabolism, acting as the body’s energy regulator. It plays a central role in appetite control, fat storage, and overall body weight management. Despite its vital function, leptin resistance—a condition where the body becomes unresponsive to leptin—has become a significant factor in the obesity epidemic.
In this article, we will take a deep scientific and medical look at leptin: what it is, how it works, what causes leptin resistance, and why it leads to weight gain. We will also examine how leptin affects men and women differently and whether one gender is more susceptible to its dysfunction.
1. What is Leptin?
Leptin is a hormone primarily secreted by fat cells (adipocytes) and is often referred to as the “satiety hormone” or “starvation hormone.” It was first discovered in 1994 and has since been recognized as a crucial component of the hypothalamic regulation of energy balance.
Leptin’s primary function is to communicate with the brain, particularly the hypothalamus, signaling when the body has enough stored fat and reducing hunger accordingly. Essentially, it serves as a feedback loop between fat stores and the brain to prevent both excessive weight gain and starvation.
How Leptin Works in the Body:
- Fat cells release leptin into the bloodstream.
- Leptin travels to the brain (hypothalamus) and signals satiety (fullness).
- When leptin levels are high, the brain understands that energy stores are sufficient, leading to reduced appetite and increased energy expenditure.
- When leptin levels are low, the brain perceives a state of starvation, triggering hunger and reducing energy expenditure to conserve fat.
This system is designed for survival. In an ideal situation, it prevents excessive weight gain by curbing appetite and prevents excessive weight loss by increasing hunger when energy stores are low.
However, in modern humans, this system is severely disrupted.
2. What is Leptin Used For?
Leptin is not just about appetite control; it has far-reaching effects in various physiological processes:
A. Regulating Metabolism & Energy Balance
- Leptin tells the body how much energy is available and whether it needs to burn or store fat.
- It increases thermogenesis (heat production), helping in fat oxidation.
- In a calorie surplus, it tells the body to increase energy expenditure; in a deficit, it does the opposite.
B. Controlling Appetite and Satiety
- High leptin = Less hunger
- Low leptin = More hunger
- When working correctly, it prevents excessive eating and promotes weight stability.
C. Regulating Hormones & Reproduction
- Leptin interacts with reproductive hormones. In women, extremely low leptin levels (from excessive weight loss or starvation) can stop menstruation (amenorrhea), affecting fertility.
- In men, leptin influences testosterone levels and metabolism.
D. Immune System and Inflammation
- Leptin plays a role in immune function and inflammation, linking obesity to chronic diseases like diabetes and cardiovascular conditions.
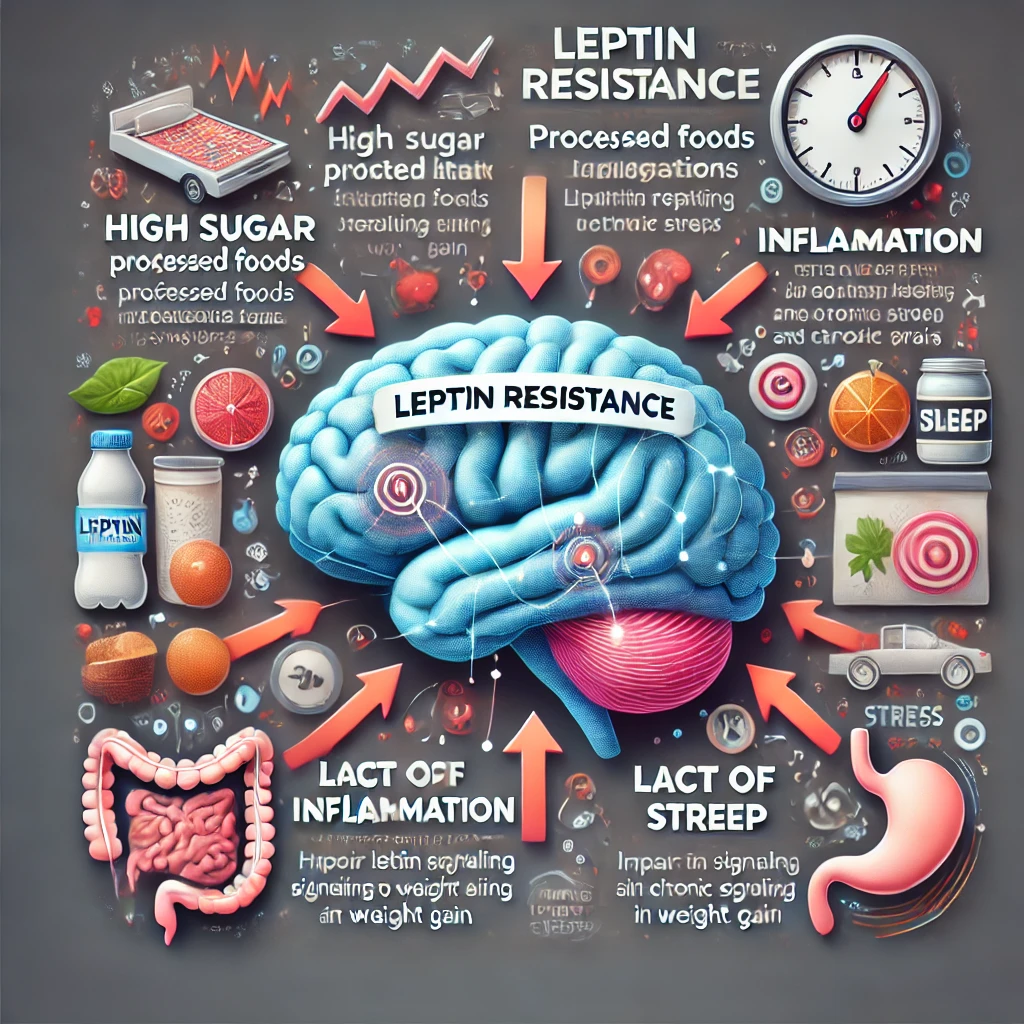
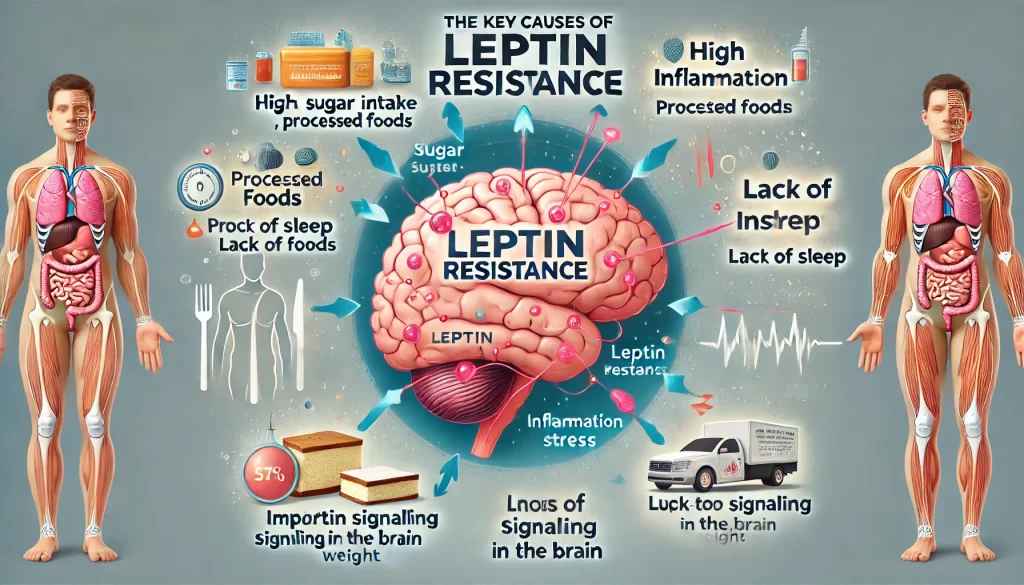
3. What Causes Leptin Resistance?
Leptin resistance is the primary reason why people gain weight despite having high leptin levels. It means the brain no longer responds properly to leptin’s signals.
How Does Leptin Resistance Develop?
Despite having high levels of leptin due to increased fat stores, the brain fails to recognize it. As a result:
- The brain thinks the body is starving and triggers hunger signals.
- It reduces metabolism to conserve energy.
- The person eats more than necessary, leading to further weight gain.
Major Causes of Leptin Resistance:
- Chronic Overeating & Processed Foods
- Diets high in sugar, processed foods, and refined carbohydrates lead to chronic insulin spikes, which impair leptin signaling.
- Inflammation
- Inflammation in the hypothalamus (caused by excessive fat accumulation and poor diet) damages leptin receptors.
- High Triglycerides
- Elevated blood triglycerides (often due to excessive sugar and processed foods) block leptin from crossing the blood-brain barrier, making it ineffective.
- Lack of Sleep
- Sleep deprivation lowers leptin levels and increases ghrelin (the hunger hormone), leading to overeating.
- Chronic Stress & Cortisol
- Chronic stress increases cortisol levels, which worsens leptin resistance and promotes fat storage, particularly in the belly area.
4. How Leptin Resistance Causes Weight Gain
Leptin resistance tricks the brain into thinking it is starving, even when fat stores are abundant. The result? Constant hunger, slower metabolism, and weight gain.
The Cycle of Leptin Resistance and Obesity:
- Weight gain leads to higher leptin levels.
- Leptin resistance develops in the brain.
- Brain thinks energy stores are low and increases appetite.
- Person eats more, gaining even more fat.
- Cycle repeats, leading to obesity.
This is why simply reducing calories does not work long-term for most people with obesity. The brain fights back by making them hungrier and slowing their metabolism.
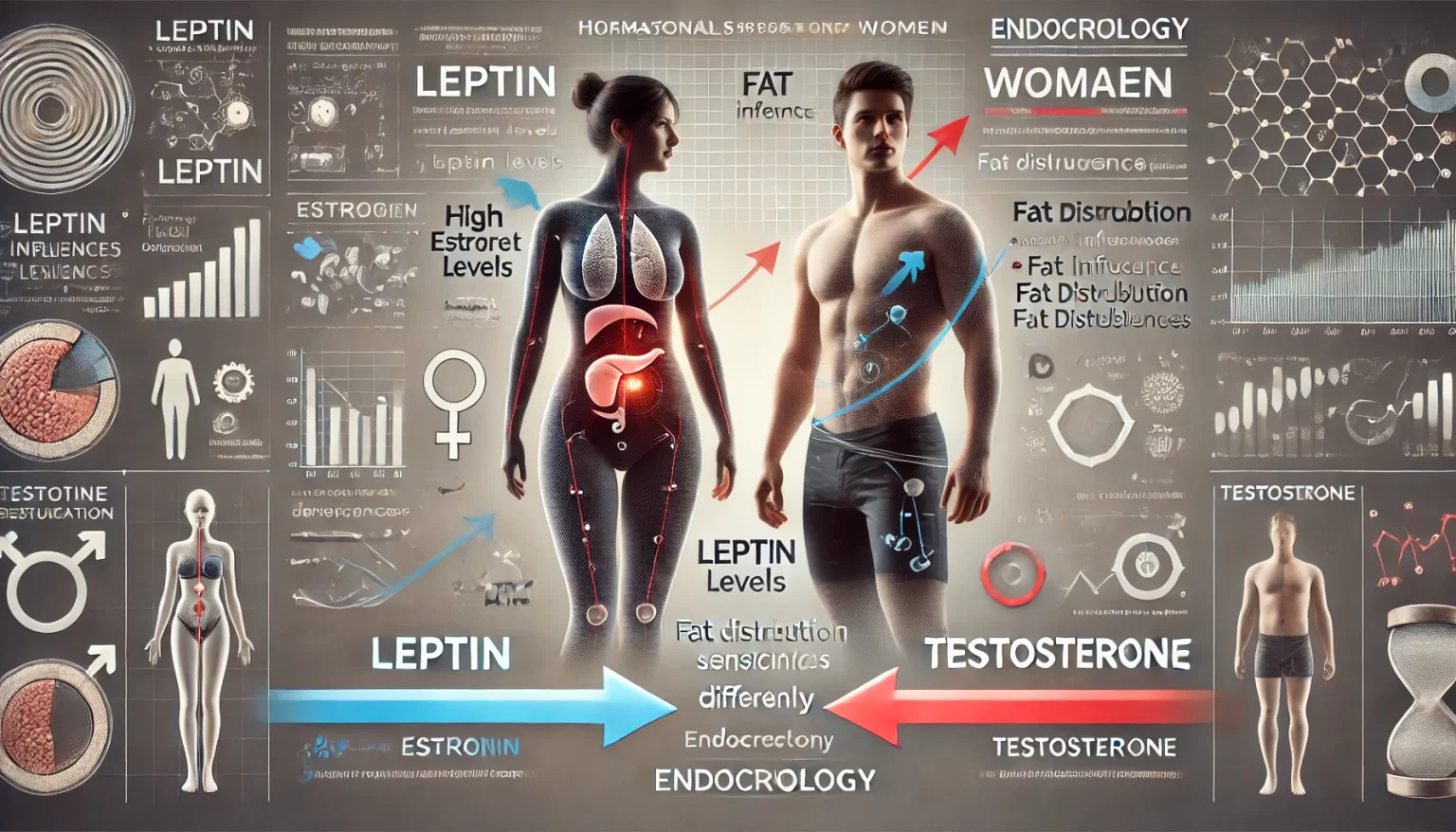
5. Does Leptin Affect Men and Women Differently?
Yes, leptin functions differently in men and women, largely due to hormonal differences.
Women Have Higher Leptin Levels than Men
- Women naturally have 2-3 times more leptin than men due to higher body fat percentages.
- Estrogen increases leptin sensitivity, which is why women tend to regulate their weight better before menopause.
Why Do Women Struggle More with Leptin After Menopause?
- Estrogen declines, leading to increased leptin resistance.
- Fat storage shifts from hips to belly, leading to metabolic issues.
- Leptin dysfunction contributes to post-menopausal weight gain.
Men & Leptin Sensitivity
- Testosterone helps keep leptin levels lower, which is why men tend to have better metabolic flexibility and lose weight faster.
- However, as men age, testosterone declines, which increases leptin resistance and fat accumulation.
Conclusion: While both genders experience leptin dysfunction, women tend to struggle more due to hormonal fluctuations, particularly after menopause.
6. How to Fix Leptin Resistance & Lose Weight Efficiently
- Reduce Processed Foods and Sugar – Lowers triglycerides and inflammation.
- Eat More Protein and Healthy Fats – Helps regulate hunger hormones.
- Improve Sleep Quality – Essential for proper leptin function.
- Exercise Regularly – Resistance training improves leptin sensitivity.
- Intermittent Fasting – Helps reset leptin levels and insulin response.
- Reduce Stress – Chronic cortisol disrupts leptin signaling.
Final Thoughts
Leptin is the master regulator of metabolism, and leptin resistance is a major cause of obesity. Understanding how leptin functions scientifically and medically helps us make informed choices about diet, exercise, and overall metabolic health.
Leptin resistance is not a willpower issue—it is a biological dysfunction that requires strategic lifestyle changes to correct. By addressing the root causes, we can restore leptin function, regulate appetite, and achieve sustainable weight loss.