Introduction
Maintaining satiety for extended periods is crucial for weight management, metabolic health, and overall well-being. Fiber-rich foods play a significant role in this process due to their ability to slow digestion, regulate blood sugar, and promote gut health. In this article, we explore the most effective fiber sources that enhance satiety, drawing on insights from nutrition science and medicine.
How Fiber Promotes Satiety
Fiber is a type of carbohydrate that the body cannot digest, yet it is essential for optimal metabolic function. It falls into two main categories:
- Soluble fiber: Dissolves in water to form a gel-like substance, slowing digestion and stabilizing blood glucose levels.
- Insoluble fiber: Adds bulk to stool, aiding in digestion and reducing hunger by physically filling the stomach.
Several mechanisms explain how fiber contributes to prolonged satiety:
- Delayed Gastric Emptying: Fiber slows the rate at which food leaves the stomach, extending feelings of fullness.
- Gut Microbiota Interaction: Soluble fiber is fermented by gut bacteria, producing short-chain fatty acids (SCFAs) that regulate hunger hormones.
- Blood Sugar Stabilization: Fiber moderates glucose absorption, preventing the spikes and crashes that can lead to increased hunger.
- Increased Chewing Time: Fiber-rich foods require more mastication, promoting satiety signals in the brain.

Top Fiber-Rich Foods for Satiety
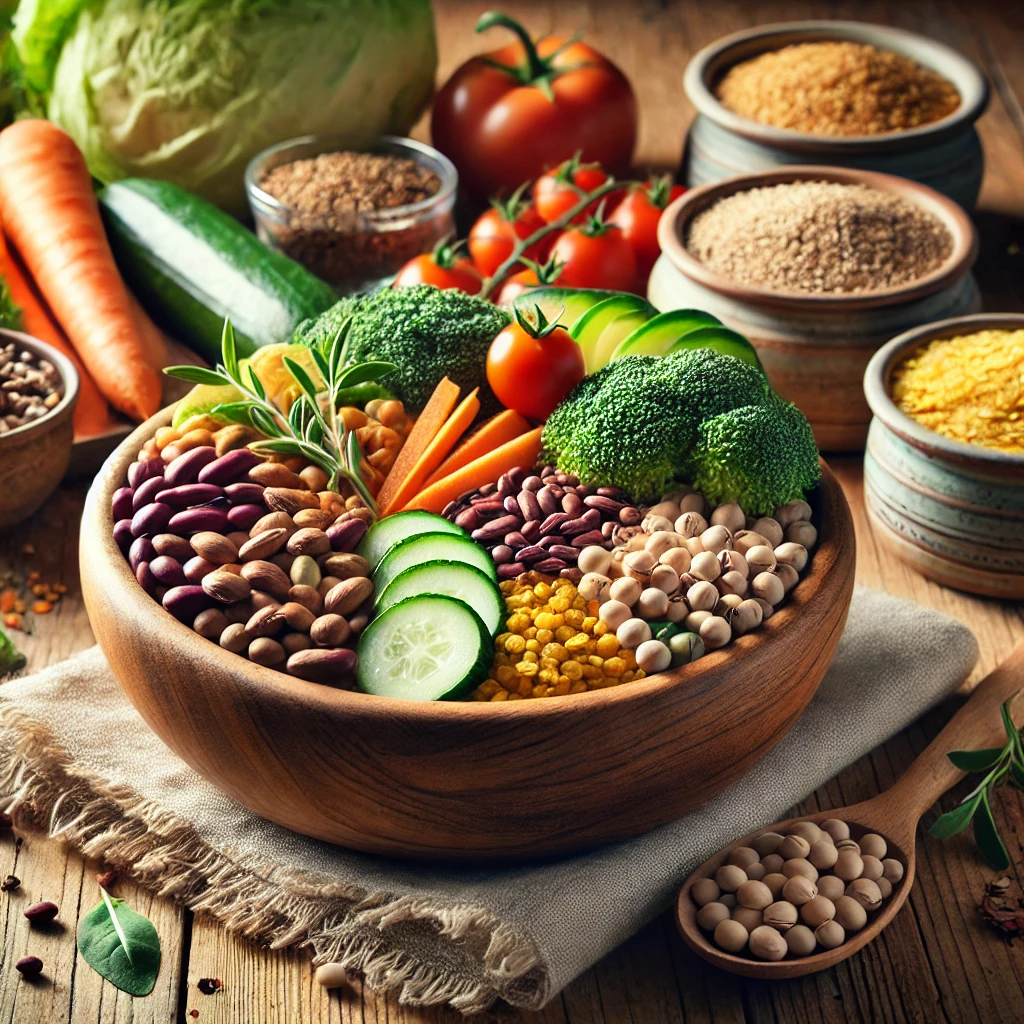
1. Legumes (Beans, Lentils, Chickpeas)
- Scientific Insight: Legumes are rich in both soluble and insoluble fiber, with 15-20g of fiber per cup. Studies suggest that legumes enhance satiety by increasing peptide YY (PYY) and glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1), hormones that regulate hunger.
- Nutritional Highlights: High in protein, iron, and resistant starch, which further promotes gut health.
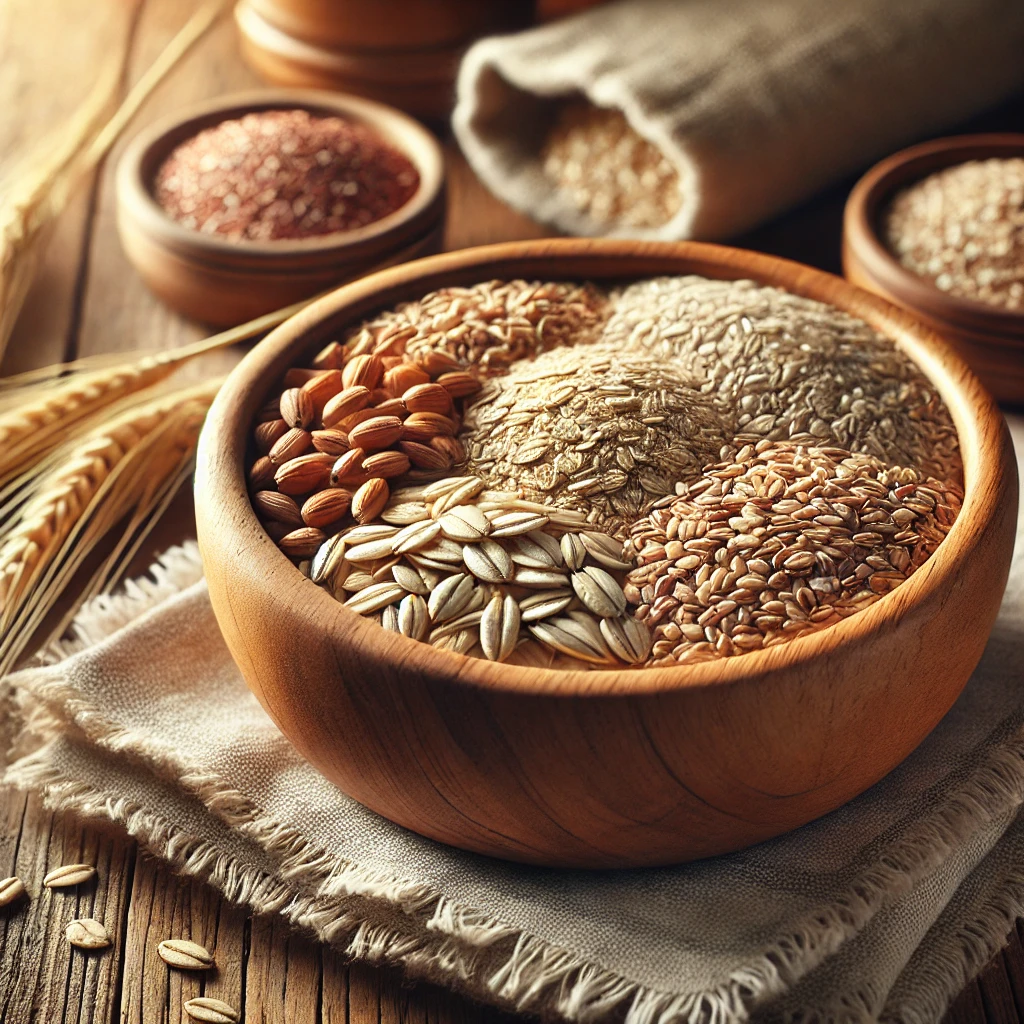
2. Whole Grains (Oats, Quinoa, Barley)
- Scientific Insight: Whole grains contain beta-glucan, a soluble fiber known to enhance satiety and improve lipid metabolism.
- Nutritional Highlights: Oats provide about 10g of fiber per cup, helping in cholesterol reduction and weight management.

3. Vegetables (Broccoli, Carrots, Brussels Sprouts)
- Scientific Insight: Vegetables are low in calories but high in fiber and water content, creating a volumetric effect that reduces overall calorie intake.
- Nutritional Highlights: Cruciferous vegetables, like broccoli, contain 5g of fiber per cup and have additional benefits in reducing inflammation and oxidative stress.
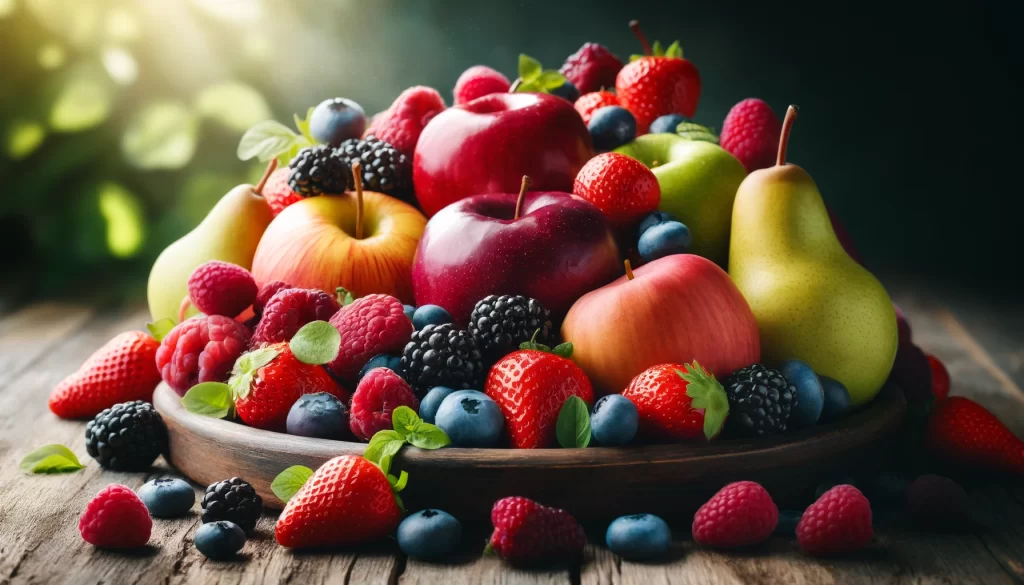
4. Fruits (Apples, Pears, Berries)
- Scientific Insight: Fruits contain both soluble fiber (pectin) and water, contributing to prolonged digestion and steady energy release.
- Nutritional Highlights: Berries provide 6-8g of fiber per cup, while apples and pears contain 4-5g each, making them ideal for sustained energy.

5. Nuts and Seeds (Chia Seeds, Flaxseeds, Almonds)
- Scientific Insight: These foods contain high amounts of fiber and healthy fats, promoting satiety through slow digestion and hormonal regulation.
- Nutritional Highlights: Chia seeds offer an impressive 10g of fiber per ounce, along with omega-3 fatty acids that further support metabolic health.
The Role of Fiber in Weight Management
Numerous clinical studies demonstrate that increasing fiber intake correlates with reduced calorie consumption and improved weight management. A study published in The Journal of Nutrition found that individuals who consumed more than 30g of fiber daily had significantly lower body fat percentages and BMI scores compared to those with lower fiber intake.

Medical Recommendations for Fiber Intake
The recommended daily fiber intake is:
- Men: 38g per day
- Women: 25g per day
Gradually increasing fiber intake while staying hydrated can prevent digestive discomfort. Physicians also suggest consuming a variety of fiber sources to maximize benefits.
Conclusion
Fiber-rich foods are essential for prolonged satiety, improved gut health, and overall metabolic balance. Incorporating diverse sources of fiber into daily meals not only supports digestion but also aids in weight management and chronic disease prevention.
Image Suggestions:
- A visual representation of fiber-rich foods (e.g., a bowl of legumes, whole grains, and vegetables)
- A scientific diagram of fiber digestion and its impact on satiety hormones
- A comparison chart of fiber content in different foods