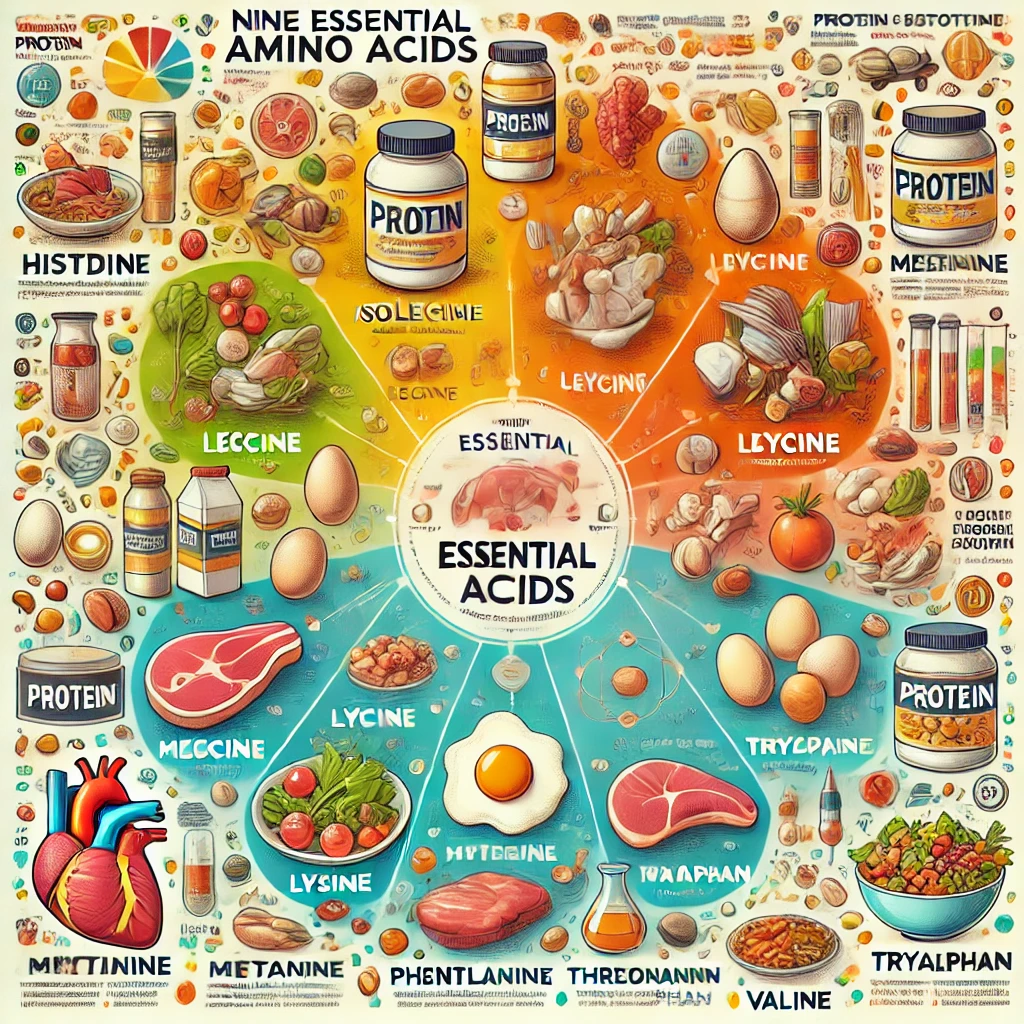
Amino acids are the building blocks of protein and play a crucial role in maintaining our overall health. Among the 20 amino acids, nine are classified as “essential” because the human body cannot produce them; they must be obtained through diet. In this article, we will explore the importance of these essential amino acids, their dietary sources, daily requirements, and the potential effects of deficiencies.
What Are the Essential Amino Acids?
The nine essential amino acids include:
- Histidine
- Isoleucine
- Leucine
- Lysine
- Methionine
- Phenylalanine
- Threonine
- Tryptophan
- Valine
These amino acids are involved in vital processes like muscle repair, immune system function, hormone production, and neurotransmitter regulation.
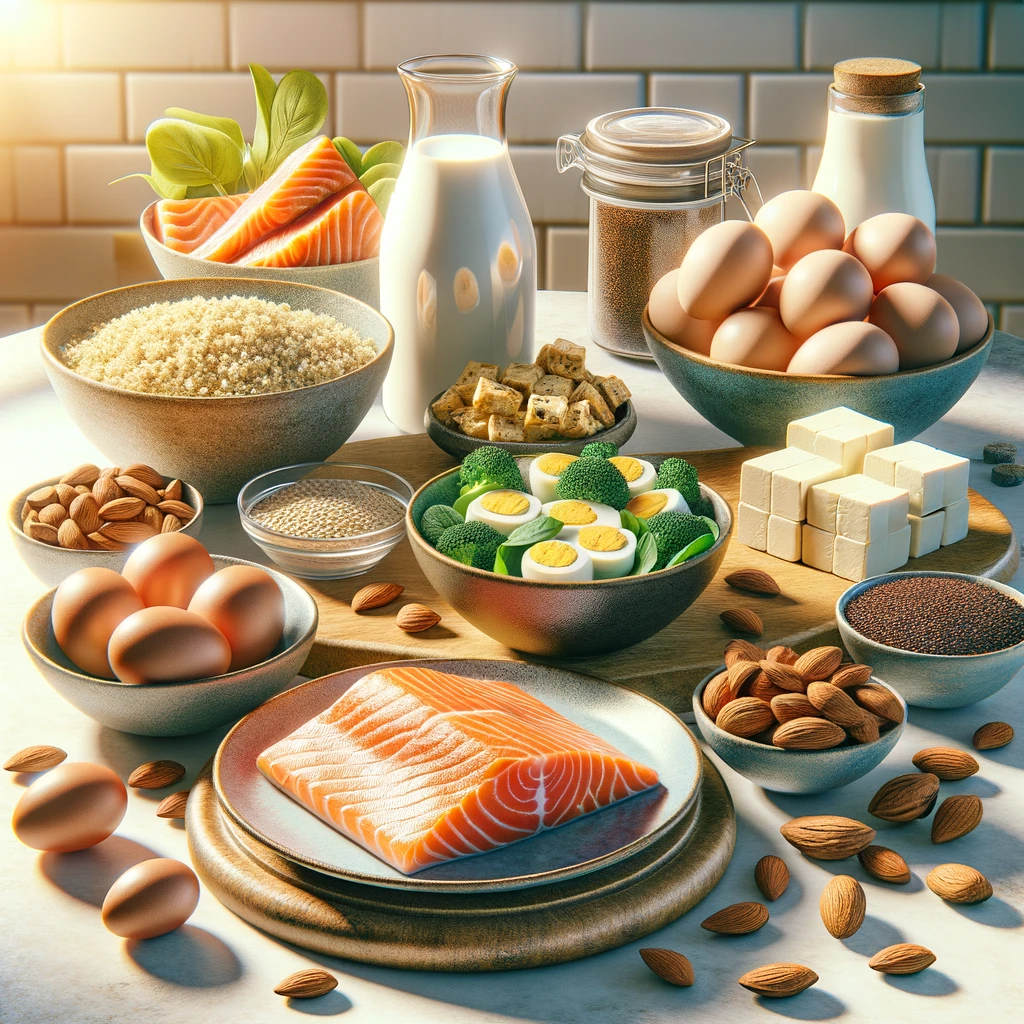
Dietary Sources of Essential Amino Acids
Including a variety of protein-rich foods in your diet ensures adequate intake of all nine essential amino acids. Below are common sources:
1. Animal-Based Sources
- Eggs: Contain a complete profile of essential amino acids.
- Meat: Beef, chicken, pork, and turkey are rich in amino acids like lysine and leucine.
- Fish: Salmon, tuna, and mackerel are excellent sources.
- Dairy: Milk, cheese, and yogurt provide essential amino acids like histidine and threonine.
2. Plant-Based Sources
- Legumes: Lentils, chickpeas, and black beans are rich in lysine.
- Grains: Quinoa and oats contain all nine essential amino acids.
- Seeds and Nuts: Sunflower seeds, almonds, and walnuts offer isoleucine and tryptophan.
- Soy Products: Tofu, tempeh, and edamame are complete protein sources.

Daily Requirements of Essential Amino Acids
The daily requirement of amino acids varies by age, sex, and activity level. The general recommended daily intake (RDI) for adults per kilogram of body weight is:
- Histidine: 10 mg/kg
- Isoleucine: 20 mg/kg
- Leucine: 39 mg/kg
- Lysine: 30 mg/kg
- Methionine (plus cysteine): 15 mg/kg
- Phenylalanine (plus tyrosine): 25 mg/kg
- Threonine: 15 mg/kg
- Tryptophan: 4 mg/kg
- Valine: 26 mg/kg
For example, a person weighing 70 kg (154 lbs) would require about 2.8 grams of leucine daily.
Effects of Essential Amino Acid Deficiencies
A deficiency in any essential amino acid can disrupt bodily functions and lead to specific symptoms:
- Histidine: Impaired hemoglobin production, anemia, and reduced neurotransmitter activity.
- Isoleucine: Fatigue, muscle weakness, and a weakened immune system.
- Leucine: Muscle wasting, difficulty with wound healing, and hypoglycemia.
- Lysine: Hair loss, irritability, and weakened bones.
- Methionine: Liver damage, skin disorders, and brittle hair and nails.
- Phenylalanine: Cognitive issues and mood disturbances.
- Threonine: Digestive problems and increased fat deposition in the liver.
- Tryptophan: Insomnia, depression, and anxiety.
- Valine: Impaired mental focus, muscle coordination issues, and sleep disturbances.
How to Ensure Adequate Intake of Essential Amino Acids
1. Diverse Diet
- Include both animal and plant-based protein sources to ensure a complete amino acid profile.
- Combine complementary proteins like rice and beans for plant-based diets.
2. Supplements
- Protein powders (whey, casein, or plant-based) can help meet daily amino acid requirements.
- BCAA (branched-chain amino acid) supplements are useful for athletes.
3. Monitor Intake
- Use nutrition tracking apps to assess daily protein and amino acid consumption.
- Consult with a dietitian or healthcare provider for personalized recommendations.
Common Myths About Amino Acids
1. You Only Need Protein, Not Individual Amino Acids
- Fact: Proteins are broken down into amino acids; adequate intake of essential amino acids is vital.
2. Plant Proteins Are Incomplete
- Fact: While some plant proteins lack one or more essential amino acids, combining sources like grains and legumes ensures a complete profile.
3. High-Protein Diets Are Harmful
- Fact: For most healthy individuals, high-protein diets are safe and beneficial when balanced.
Conclusion
Essential amino acids are fundamental to our health and well-being. By understanding their sources, daily requirements, and the impact of deficiencies, you can optimize your diet to meet your body’s needs. Whether you’re an athlete or simply looking to improve your overall health, prioritizing amino acid intake is crucial. A balanced diet rich in diverse protein sources is the best way to ensure you get all nine essential amino acids.